Dry Transformer VS Oil Transformer
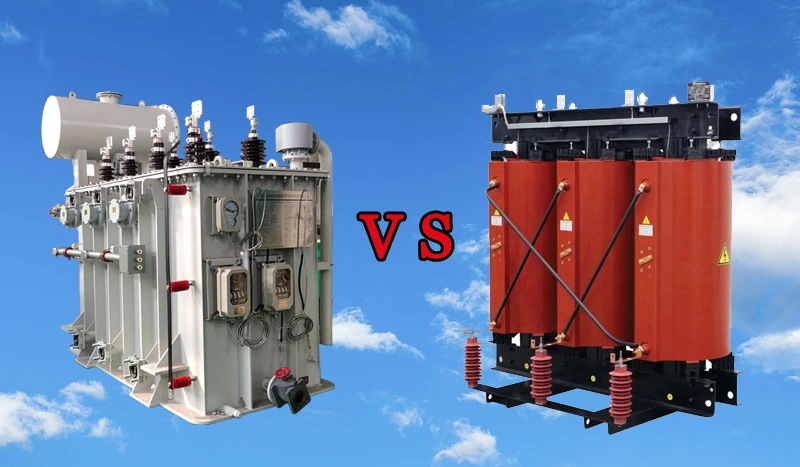
Transformers are devices that help electricity flow efficiently. This article will detail the difference between the two most common types of transformers: dry type and oil transformer.
Daelim is a professional top transformer supplier. Provide Oil Transformer and Dry Type Transformer. Many years of international project experience allow Daelim to design a variety of international standard transformers. The transformer has good quality and has certificates such as UL/CUL, CSA, and CESI.
Small-substastion Transformer
Single Phase Pole Mounted Transformer
Oil Immersed Power Transformer
Table of Content
What Is The Purpose Of An Oil Transformer?
An oil-filled transformer is a voltage transformer that cools the oil inside to lower the temperature. Its body is typically mounted on a large welded steel tank filled with insulation oil.
The oil-based transformer uses insulators for high-voltage electrical parts like switches, condensers, converters, and circuit breakers. Once the device is switched on, the coil and iron core heat is converted into insulation oil, transforming it into a cooling agent.
Transmission lines and electrical substations frequently use transformers that operate on oil. Its core and coils are cooled and insulated by submerging them in oil. In a convection-driven system, oil circulates via ducts in the coil and then wraps around the core.
When the capacity of the tank is low, air flow from outside the container cools the oil.
In greater ratings, an air-cooled radiator serves as the oil’s cooling source.
Generally, transformer oils are made to function well at extremely high temperatures, insulating, cooling, and preventing corona discharges and overheating.
What’s Inside An Oil Transformer?
Iron Center
The transformer’s iron core is the principal magnetic link, and it is the component capable of magnetism conductance. It transforms the magnetic energy into electrical energy for the secondary circuit and the electric power of the main circuit into magnetic energy.
Typically, silicon steel sheets are arranged to form the iron core of a transformer, and they are isolated from one another. The silicon steel sheet mostly influences the transformer’s no-load loss.
Transformer Loop
The primary winding and the secondary winding are two different windings that make up any type of transformer. The primary winding is connected to the power source, and the secondary winding is connected to the load.
Within the same iron core column, the first and second windings of every phase of a three-phase transformer are wrapped into cylindrical shapes. The low-voltage winding can easily isolate the core in this position.
A space is left between the high and low windings to serve as an oil route, which allows the transformer oil to circulate and help in thermal transfer.
Oil Conservator
The transformer oil conservator is also known as the oil pillow since it resembles a cylindrical pillow. It is mounted horizontally above the oil reservoir and is pumped into the transformer’s oil tank.
Typically, the capacity of the oil conservator is 10% or less of the volume of the storage tanks.
Once the transformer oil is heated and expands, it moves from the oil tank into the oil conservator; the transformer oil contracts once it’s cold and is refilled from the oil conservator to the oil reservoir.
Transformer Bushing
The guide rod serves as the connection between the transformer winding lead wire and the external circuit. The transformer bushing is an insulator between the guide rods and the box lid and keeps the guide rod in place.
Transformer Breather
Power transformer protection includes the use of pressure relief equipment. If an internal defect or short circuit arises in an oil-immersed transformer, arcing will immediately evaporate the oil, causing the temperature in the transformer tank to rise rapidly.
It is necessary to take precautionary measures because if the pressure is not released immediately, the oil tank can break, resulting in an explosion and fire.
Tap Changer
When utilized for the on-load voltage-controlling transformer, the oil conservator has a switch oil conservator placed at the bottom without capsules called the tap changer.
Oil Purifier
The oil purifier is an installation on the sidewall of the transformer or the lower portion of the strong oil cooler that contains an adsorbent: silica gel or activated alumina.
Read more: Electrical transformer
What Is The Advantage Of An Oil Transformer?
- An oil transformer typically costs 0.5 to 1 times less than a dry transformer and holds the same capacity.
- Oil transformers are also more adaptable to the grid system. It covers the need for power distribution from the transitional station to the terminal site.
- The insulating material of an oil transformer doesn’t rust immediately and dries out with time. It isn’t prone to damage.
What Is The Disadvantage Of An Oil Transformer?
- Despite having the benefit of heat dissipation, the cooling oil in an oil transformer easily burns and explodes. There is a high risk of environmental pollution caused by engine oil spills if the transformer explodes.
- Oil transformers are not fire-resistant. It isn’t a great transformer in specific locations such as hospitals, malls, workplaces, underground structures, and places with strict fire safety regulations.
- Oil transformer maintenance can be costly since you have to check the oil volume, make oil changes, do oil aging, and oil leaks periodically.
What Is The Function Of A Dry Transformer?
A dry transformer is also called a cast resin transformer due to its solid structure. The device has no rotating parts. This makes dry transformers the best for environmentally beneficial temperature insulation technologies.
In contrast to liquid-type transformers, which rely on other components such as fire or oil to function, the operation of a dry transformer only requires a change in the voltage.
On the other hand, dry transformers employ cool air rather than liquid as their medium instead of other types of transformers. If a dry transformer is stored in a room with good ventilation, it will not be difficult for the coils to cool again.
If you use a dry transformer, as opposed to a conventional liquid transformer, you do not have to keep it in watersheds or vaults capable of withstanding fire.
Moreover, they don’t create any toxic gasses, making them environmentally beneficial even for indoor installation.
Since they can satisfy both low-voltage and high-voltage needs effortlessly, dry transformers are utilized frequently in the industrial, commercial, and sometimes even governmental sectors.
What’s Inside A Dry Transformer?
Cast-Resin
The dry transformers are cooled by using natural airflow as the cooling medium. However, to use forced air cooling, fans are required. The cooling provided by the fan brings the temperature of the transformer down to the desired level. The vents should be clear to ensure that the natural temperature transmission from the transformer can take place.
Core
The core provides stability for the windings of the transformer and creates a low-reluctance channel for the magnetic force. Usually, the laminated soft iron core is used in their construction to minimize energy reduction.
Insulating Material
Manufacturers utilize insulating materials to separate the transformer windings from the transformer core.
Additionally, copper produces these windings due to their high conductivity and malleability. The high conduction qualities minimize copper and energy waste; this makes the conductor bend into a close coil around the core due to its great elasticity.
Tap Changer
Tap changer switches with changing voltage positions. Its main purpose is to modify a transformer’s output voltage. You can adjust the ratio between the voltage level by moving the tap changer.
Tap changers come in two varieties: DETC de-energized tap changer (DETC) and on-load (LTC).
Windings
Electrical wire, known as windings, is used in the coils and inductors of transformers. Manufacturers classify them based on how easily they can be produced and how well they work in electric systems.
Specialists typically divide windings with a voltage range into main and secondary windings. The supply determines the primary windings, whereas the voltage range determines the secondary windings.
The parts or features of a dry transformer winding can vary depending on the manufacturer.
Can Dry-Type Transformers Be Installed Without The Enclosure?
Dry-type transformers installed outdoors need an enclosure. A dry-type transformer must be installed in a waterproof enclosure before being used outdoors.
If the transformer is over 112.5 kVA, it must have insulation of Class 155 or greater and be entirely enclosed, save from ventilation openings, before it can be placed within 1 foot of combustible construction materials
What Is The Efficiency Of A Dry-Type Transformer?
In the electricity transmission and transformation sector, where energy consumption is high, the transformer business has enormous potential for energy savings. A key strategy for power conservation and emission reduction is to increase the energy efficiency of transformers.
Dry-type transformers are among the essential pieces of equipment for converting, distributing, and regulating electrical currents. In actuality, energy losses, including heat, electromechanical, and electromagnetic losses, occur during the conversion of electrical energy.
Therefore, the effectiveness of energy conversion of dry transformers depends on the changes in AC voltage from one value to another while maintaining the same frequency.
What Are The Advantages Of A Dry-Type Transformer?
- The dry-type transformer is safe for people and properties.
- Installation is simple, and maintenance is easy with a pollution-free solution.
- It’s environmentally friendly and has less side clearance.
- It has an excellent capacity to withstand overloads.
- It has reduced costs for fire prevention systems and civil installation work.
- Excellent response to earthquake occurrences.
- High short circuit current resistance.
- It’s suitable for polluted and moist environments.
What Are The Disadvantages Of A Dry-Type Transformer?
- A dry-type transformer lasts a long time and has fewer winding failures. However, if it fails, the entire setup must be altered, including replacing both the high-voltage and low-voltage windings with legs.
- When comparing transformers of identical voltage and power ratings, dry-type transformers are far more pricey.
Keep reading: 3 Phase Transformer Power Transformer Manufacturer
What Is The Difference Between An Oil Transformer And A Dry Transformer?
Price
In most cases, oil-filled transformers are more cost-effective than their dry counterparts. However, the pricing might still be somewhat variable based on the features of the transformers.
Cooling Agent
The proper installation of the cooling medium is essential to stop the transformer from overheating, which could result in an explosion or fire. Transformers will overheat under stress, but this problem needs to be fixed because temperature increases are not allowed when using transformers.
When it comes to oil-filled transformers, the air is deployed as the cooling agent, while dry-type transformers utilize air as their cooling system.
Since oil-filled transformers offer a high fire risk, dry-type transformers are used in certain public areas instead of their oil-filled counterparts. As a result, they are only limited to outdoor installations.
The safer alternative is dry-type transformers, which are common in public areas like business centers and transportation hubs.
Efficiency
Oil-filled transformers offer a greater capacity than dry-type transformers, which are limited in size and the operating voltage they can handle. The efficiency of oil-filled transformers is higher than dry-type transformers, which have size and voltage rating restrictions.
Sound Operating Capacity
Transformers, in general, produce a great deal of noise whenever they are put into operation, and oil-filled transformers are noticeably louder than dry-type transformers.
What Is The Difference Between Indoor And Outdoor Transformers?
The structure of indoor versus outdoor units differs significantly, despite the instrument transformer’s identical function.
Outdoor transformers must be shielded from the elements, including any potential pollutants. This implies that the material used to construct outdoor units should be able to reduce tracking.
Meanwhile, indoor transformers are created for indoor use and convert line voltage input to the low voltage output.
Indoor transformers have a proper roof covering them in the process sector, while outdoor transformers are only used for distribution.
Should I Choose A Dry Transformer Or An Oil Transformer?
Before choosing between a dry or an oil transformer, you must consider the following factors.
Operational Fee
The operational losses of dry-type transformers are significantly higher than oil-cooled transformers.
In contrast, oil-cooled transformers are better in terms of efficiency. They also have longer lifespans.
Location
Selecting a transformer is very crucial. It is generally agreed that dry-type transformers are harmless to the environment because they do not pose a fire risk when used in indoor applications.
Due to the potential for oil leakage, which could result in a fire, oil-cooled transformers are best suited for installation in outdoor settings.
Recyclability
When they reach the end of their service life, dry-type transformers have significantly fewer alternatives for recycling their cores and coils than oil-type units.
Oil-cooled devices have a longer operating life and are easier to maintain, so not only do they generate less waste, but they also require lesser repairs.
You may enjoy: How power transformers be manufactured, tested & delivered?
Conclusion
Transformers filled with oil appear to be the most favorable option in terms of energy savings, reduced cost, and the use of recyclable materials.
On the other hand, dry-type transformers are regarded as being safer for use in internal operations. Always do business with a reliable provider who offers the highest quality dry-type and oil-filled transformers in their inventory.
Download Resource
About Daelim
Recent Posts
About Bin Dong

Transformers are devices that help electricity flow efficiently. This article will detail the difference between the two most common types of transformers: dry type and oil transformer.
Daelim is a professional top transformer supplier. Provide Oil Transformer and Dry Type Transformer. Many years of international project experience allow Daelim to design a variety of international standard transformers. The transformer has good quality and has certificates such as UL/CUL, CSA, and CESI.
Small-substastion Transformer
Single Phase Pole Mounted Transformer
Oil Immersed Power Transformer
Table of Content
What Is The Purpose Of An Oil Transformer?
An oil-filled transformer is a voltage transformer that cools the oil inside to lower the temperature. Its body is typically mounted on a large welded steel tank filled with insulation oil.
The oil-based transformer uses insulators for high-voltage electrical parts like switches, condensers, converters, and circuit breakers. Once the device is switched on, the coil and iron core heat is converted into insulation oil, transforming it into a cooling agent.
Transmission lines and electrical substations frequently use transformers that operate on oil. Its core and coils are cooled and insulated by submerging them in oil. In a convection-driven system, oil circulates via ducts in the coil and then wraps around the core.
When the capacity of the tank is low, air flow from outside the container cools the oil.
In greater ratings, an air-cooled radiator serves as the oil’s cooling source.
Generally, transformer oils are made to function well at extremely high temperatures, insulating, cooling, and preventing corona discharges and overheating.
What’s Inside An Oil Transformer?
Iron Center
The transformer’s iron core is the principal magnetic link, and it is the component capable of magnetism conductance. It transforms the magnetic energy into electrical energy for the secondary circuit and the electric power of the main circuit into magnetic energy.
Typically, silicon steel sheets are arranged to form the iron core of a transformer, and they are isolated from one another. The silicon steel sheet mostly influences the transformer’s no-load loss.
Transformer Loop
The primary winding and the secondary winding are two different windings that make up any type of transformer. The primary winding is connected to the power source, and the secondary winding is connected to the load.
Within the same iron core column, the first and second windings of every phase of a three-phase transformer are wrapped into cylindrical shapes. The low-voltage winding can easily isolate the core in this position.
A space is left between the high and low windings to serve as an oil route, which allows the transformer oil to circulate and help in thermal transfer.
Oil Conservator
The transformer oil conservator is also known as the oil pillow since it resembles a cylindrical pillow. It is mounted horizontally above the oil reservoir and is pumped into the transformer’s oil tank.
Typically, the capacity of the oil conservator is 10% or less of the volume of the storage tanks.
Once the transformer oil is heated and expands, it moves from the oil tank into the oil conservator; the transformer oil contracts once it’s cold and is refilled from the oil conservator to the oil reservoir.
Transformer Bushing
The guide rod serves as the connection between the transformer winding lead wire and the external circuit. The transformer bushing is an insulator between the guide rods and the box lid and keeps the guide rod in place.
Transformer Breather
Power transformer protection includes the use of pressure relief equipment. If an internal defect or short circuit arises in an oil-immersed transformer, arcing will immediately evaporate the oil, causing the temperature in the transformer tank to rise rapidly.
It is necessary to take precautionary measures because if the pressure is not released immediately, the oil tank can break, resulting in an explosion and fire.
Tap Changer
When utilized for the on-load voltage-controlling transformer, the oil conservator has a switch oil conservator placed at the bottom without capsules called the tap changer.
Oil Purifier
The oil purifier is an installation on the sidewall of the transformer or the lower portion of the strong oil cooler that contains an adsorbent: silica gel or activated alumina.
What Is The Advantage Of An Oil Transformer?
- An oil transformer typically costs 0.5 to 1 times less than a dry transformer and holds the same capacity.
- Oil transformers are also more adaptable to the grid system. It covers the need for power distribution from the transitional station to the terminal site.
- The insulating material of an oil transformer doesn’t rust immediately and dries out with time. It isn’t prone to damage.
What Is The Disadvantage Of An Oil Transformer?
- Despite having the benefit of heat dissipation, the cooling oil in an oil transformer easily burns and explodes. There is a high risk of environmental pollution caused by engine oil spills if the transformer explodes.
- Oil transformers are not fire-resistant. It isn’t a great transformer in specific locations such as hospitals, malls, workplaces, underground structures, and places with strict fire safety regulations.
- Oil transformer maintenance can be costly since you have to check the oil volume, make oil changes, do oil aging, and oil leaks periodically.
What Is The Function Of A Dry Transformer?
A dry transformer is also called a cast resin transformer due to its solid structure. The device has no rotating parts. This makes dry transformers the best for environmentally beneficial temperature insulation technologies.
In contrast to liquid-type transformers, which rely on other components such as fire or oil to function, the operation of a dry transformer only requires a change in the voltage.
On the other hand, dry transformers employ cool air rather than liquid as their medium instead of other types of transformers. If a dry transformer is stored in a room with good ventilation, it will not be difficult for the coils to cool again.
If you use a dry transformer, as opposed to a conventional liquid transformer, you do not have to keep it in watersheds or vaults capable of withstanding fire.
Moreover, they don’t create any toxic gasses, making them environmentally beneficial even for indoor installation.
Since they can satisfy both low-voltage and high-voltage needs effortlessly, dry transformers are utilized frequently in the industrial, commercial, and sometimes even governmental sectors.
What’s Inside A Dry Transformer?
Cast-Resin
The dry transformers are cooled by using natural airflow as the cooling medium. However, to use forced air cooling, fans are required. The cooling provided by the fan brings the temperature of the transformer down to the desired level. The vents should be clear to ensure that the natural temperature transmission from the transformer can take place.
Core
The core provides stability for the windings of the transformer and creates a low-reluctance channel for the magnetic force. Usually, the laminated soft iron core is used in their construction to minimize energy reduction.
Insulating Material
Manufacturers utilize insulating materials to separate the transformer windings from the transformer core.
Additionally, copper produces these windings due to their high conductivity and malleability. The high conduction qualities minimize copper and energy waste; this makes the conductor bend into a close coil around the core due to its great elasticity.
Tap Changer
Tap changer switches with changing voltage positions. Its main purpose is to modify a transformer’s output voltage. You can adjust the ratio between the voltage level by moving the tap changer.
Tap changers come in two varieties: DETC de-energized tap changer (DETC) and on-load (LTC).
Windings
Electrical wire, known as windings, is used in the coils and inductors of transformers. Manufacturers classify them based on how easily they can be produced and how well they work in electric systems.
Specialists typically divide windings with a voltage range into main and secondary windings. The supply determines the primary windings, whereas the voltage range determines the secondary windings.
The parts or features of a dry transformer winding can vary depending on the manufacturer.
Can Dry-Type Transformers Be Installed Without The Enclosure?
Dry-type transformers installed outdoors need an enclosure. A dry-type transformer must be installed in a waterproof enclosure before being used outdoors.
If the transformer is over 112.5 kVA, it must have insulation of Class 155 or greater and be entirely enclosed, save from ventilation openings, before it can be placed within 1 foot of combustible construction materials
What Is The Efficiency Of A Dry-Type Transformer?
In the electricity transmission and transformation sector, where energy consumption is high, the transformer business has enormous potential for energy savings. A key strategy for power conservation and emission reduction is to increase the energy efficiency of transformers.
Dry-type transformers are among the essential pieces of equipment for converting, distributing, and regulating electrical currents. In actuality, energy losses, including heat, electromechanical, and electromagnetic losses, occur during the conversion of electrical energy.
Therefore, the effectiveness of energy conversion of dry transformers depends on the changes in AC voltage from one value to another while maintaining the same frequency.
What Are The Advantages Of A Dry-Type Transformer?
- The dry-type transformer is safe for people and properties.
- Installation is simple, and maintenance is easy with a pollution-free solution.
- It’s environmentally friendly and has less side clearance.
- It has an excellent capacity to withstand overloads.
- It has reduced costs for fire prevention systems and civil installation work.
- Excellent response to earthquake occurrences.
- High short circuit current resistance.
- It’s suitable for polluted and moist environments.
What Are The Disadvantages Of A Dry-Type Transformer?
- A dry-type transformer lasts a long time and has fewer winding failures. However, if it fails, the entire setup must be altered, including replacing both the high-voltage and low-voltage windings with legs.
- When comparing transformers of identical voltage and power ratings, dry-type transformers are far more pricey.
What Is The Difference Between An Oil Transformer And A Dry Transformer?
Price
In most cases, oil-filled transformers are more cost-effective than their dry counterparts. However, the pricing might still be somewhat variable based on the features of the transformers.
Cooling Agent
The proper installation of the cooling medium is essential to stop the transformer from overheating, which could result in an explosion or fire. Transformers will overheat under stress, but this problem needs to be fixed because temperature increases are not allowed when using transformers.
When it comes to oil-filled transformers, the air is deployed as the cooling agent, while dry-type transformers utilize air as their cooling system.
Since oil-filled transformers offer a high fire risk, dry-type transformers are used in certain public areas instead of their oil-filled counterparts. As a result, they are only limited to outdoor installations.
The safer alternative is dry-type transformers, which are common in public areas like business centers and transportation hubs.
Efficiency
Oil-filled transformers offer a greater capacity than dry-type transformers, which are limited in size and the operating voltage they can handle. The efficiency of oil-filled transformers is higher than dry-type transformers, which have size and voltage rating restrictions.
Sound Operating Capacity
Transformers, in general, produce a great deal of noise whenever they are put into operation, and oil-filled transformers are noticeably louder than dry-type transformers.
What Is The Difference Between Indoor And Outdoor Transformers?
The structure of indoor versus outdoor units differs significantly, despite the instrument transformer’s identical function.
Outdoor transformers must be shielded from the elements, including any potential pollutants. This implies that the material used to construct outdoor units should be able to reduce tracking.
Meanwhile, indoor transformers are created for indoor use and convert line voltage input to the low voltage output.
Indoor transformers have a proper roof covering them in the process sector, while outdoor transformers are only used for distribution.
Should I Choose A Dry Transformer Or An Oil Transformer?
Before choosing between a dry or an oil transformer, you must consider the following factors.
Operational Fee
The operational losses of dry-type transformers are significantly higher than oil-cooled transformers.
In contrast, oil-cooled transformers are better in terms of efficiency. They also have longer lifespans.
Location
Selecting a transformer is very crucial. It is generally agreed that dry-type transformers are harmless to the environment because they do not pose a fire risk when used in indoor applications.
Due to the potential for oil leakage, which could result in a fire, oil-cooled transformers are best suited for installation in outdoor settings.
Recyclability
When they reach the end of their service life, dry-type transformers have significantly fewer alternatives for recycling their cores and coils than oil-type units.
Oil-cooled devices have a longer operating life and are easier to maintain, so not only do they generate less waste, but they also require lesser repairs.
Conclusion
Transformers filled with oil appear to be the most favorable option in terms of energy savings, reduced cost, and the use of recyclable materials.
On the other hand, dry-type transformers are regarded as being safer for use in internal operations. Always do business with a reliable provider who offers the highest quality dry-type and oil-filled transformers in their inventory.











